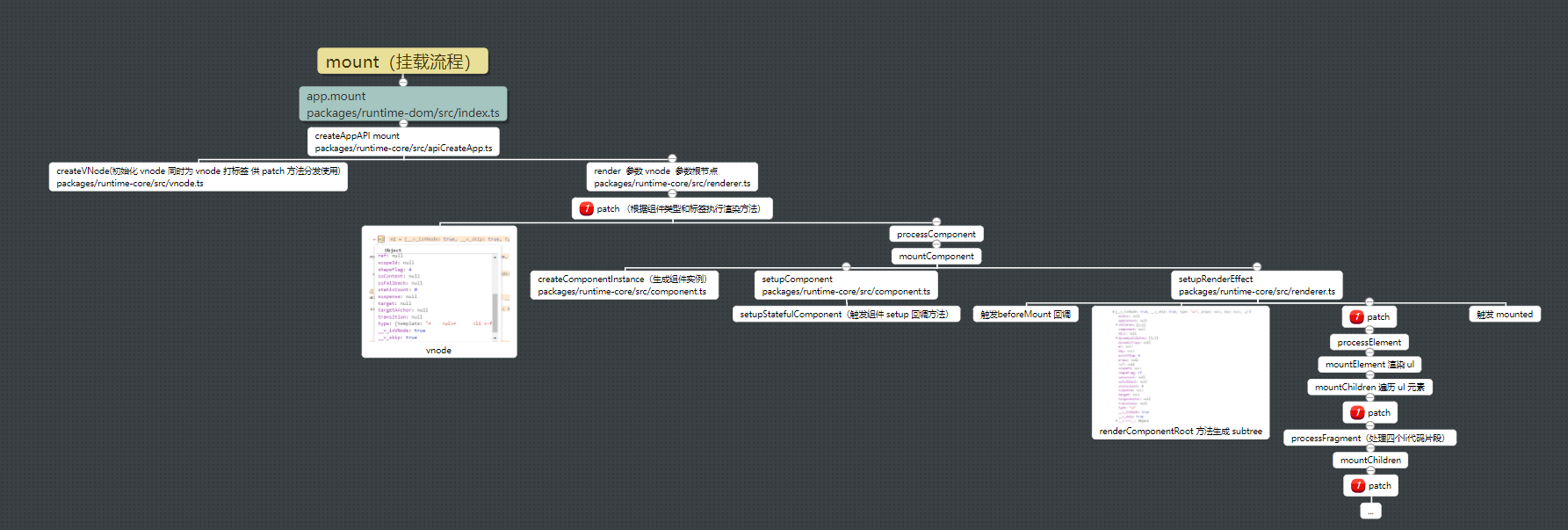
vue3 源码分析-mount
前言
Vue.createApp(App).mount('#app')
上一篇主要学习了 createApp api 的相关源码,其方法内部涉及到的 mount 方法其实是 createApp 方法内部最核心的操作,本文主要针对 mount 方法进行深入分析。
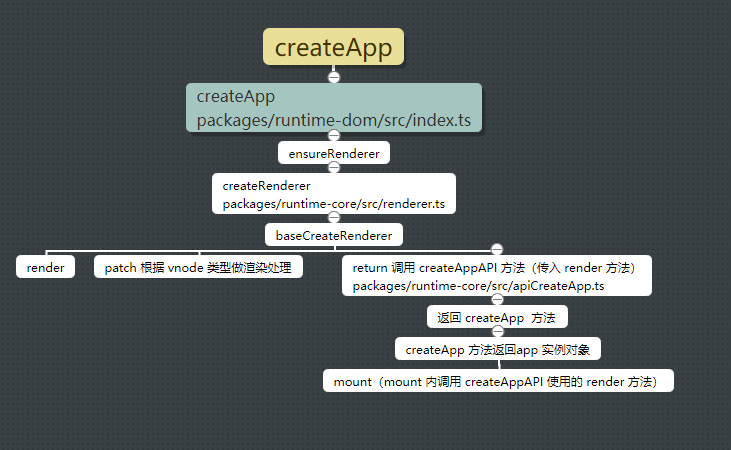
下图为 createApp 的简单流程
下载源码开启调试模式
下载项目
git clone https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next.git
更改 package.json scripts 选项
{
"dev": "node scripts/dev.js"
}
{
"dev": "node scripts/dev.js --sourcemap --environment TARGET:web-full-dev"
}
更改此配置的目的为执行 yarn run dev 时能够获取编译后的 source-map 方便打断点调试源码。
开启两个命令行终端,先后运行
yarn run dev
yarn run serve
yarn run dev 命令运行后打包的文件放置在 /packages/vue/dist/vue.global.js 可以通过 http://localhost:5000/packages/vue/dist/vue.global.js。
注:调试时确保 js 已经加载,可以将 script 引入头部(阅读源码时)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="http://localhost:5000/packages/vue/dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo"></div>
<script src="./hello.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
mount 方法
上期中主要分析了 createApp 过程,本文只要涉及 mount 方法(组件初始化挂载流程)的实现。
packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts
mount(rootContainer: HostElement, isHydrate?: boolean): any {
if (!isMounted) {
// 1. 调用 `createVNode` 方法获取 vnode, 其中 `rootComponent` 即为调用 `createApp(config)` 数据, rootProps 为其传入的对应组件的属性。使用 vnode 渲染真实的数据。
const vnode = createVNode(
rootComponent as ConcreteComponent,
rootProps
)
// 2. 保存 context 在根节点上
vnode.appContext = context
if (isHydrate && hydrate) {
hydrate(vnode as VNode<Node, Element>, rootContainer as any)
} else {
// 3.调用 rander 渲染函数
render(vnode, rootContainer)
}
// 4.isMounted 设置为 true
isMounted = true
// 5. 实例的_container保存为当前rootContainer; mount('#app')
app._container = rootContainer
// 6. rootContainer增加属性__vue_app__,置为当前app实例;
;(rootContainer as any).__vue_app__ = app
return vnode.component!.proxy
}
}
上述代码的核心渲染代码为 render 函数。
render
render 的函数目前只是负责任务分发的工作, 分发两个工作 unmount 和 patch
packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
// 1. vnode,是要更新到页面上的vnode,通过上面createVNode获得;container为展现的容器 ('#app')
const render: RootRenderFunction = (vnode, container) => {
if (vnode == null) {
// 2.如果 vnode 为空,并且container._vnode有值,也就是有之前的dom渲染,则进行unmount操作;
if (container._vnode) {
unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true)
}
} else {
// 3. 如果vnode不为空,则进行patch操作,dom diff和渲染
patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container)
}
// 4. 执行flushPostFlushCbs函数,回调调度器,使用Promise实现,与Vue2的区别是Vue2是宏任务或微任务来处理的
flushPostFlushCbs()
// 5. 把container的_vnode存储为当前vnode,方便后面进行dom diff操作
container._vnode = vnode
}
本文主要讲述 mount 组件挂在部分的源码,vnode 不会为空,肯定会走到 patch 函数部分。
packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const patch: PatchFn = (
n1, // old 组件
n2, // new 组件
container, // 容器
anchor = null,
parentComponent = null,
parentSuspense = null,
isSVG = false,
optimized = false
) => {
//...
const {type, ref, shapeFlag} = n2
switch (type) {
case Text:
// 文本
processText(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Comment:
// 注释
processCommentNode(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Static:
// 静态组件 纯html
if (n1 == null) {
mountStaticNode(n2, container, anchor, isSVG)
} else if (__DEV__) {
patchStaticNode(n1, n2, container, isSVG)
}
break
case Fragment:
// 处理片段(dom数组)的函数 多根组件
processFragment(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
break
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
// 处理 dom 元素
processElement(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
// 处理组件
processComponent(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {
// 内置组件传送 弹框
;(type as typeof TeleportImpl).process(
n1 as TeleportVNode,
n2 as TeleportVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized,
internals
)
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
// SUSPENSE 组件传送 组件异步处理状态
;(type as typeof SuspenseImpl).process(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized, internals)
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn('Invalid VNode type:', type, `(${typeof type})`)
}
}
if (ref != null && parentComponent) {
setRef(ref, n1 && n1.ref, parentComponent, parentSuspense, n2)
}
}
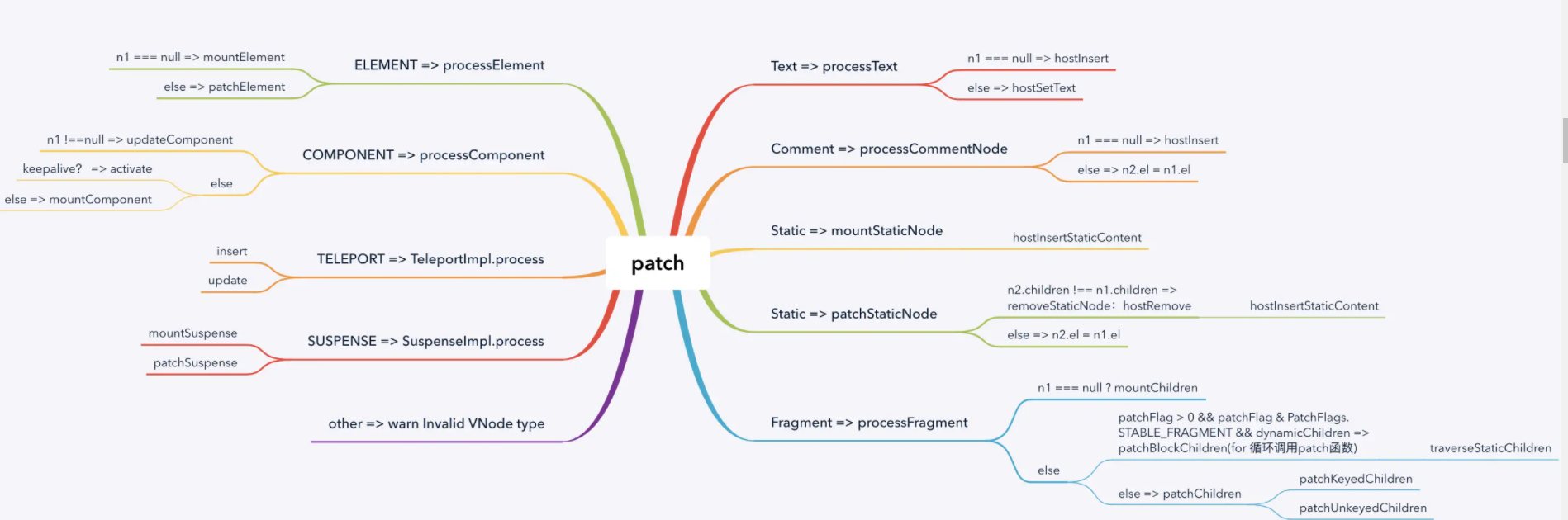
上面的图片为 patch 方法所执行各种情况, 下面会使用示例代码分析, 组件挂载的流程。
示例代码
hello.js
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
list: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'],
}
},
})
app.mount('#demo')
hello.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta
name="viewport"
content="initial-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,
user-scalable=no,target-densitydpi=medium-dpi,viewport-fit=cover"
/>
<title>Vue3.js hello example</title>
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in list" :key="item"></li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="./hello.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
代码运行后:

示例代码分析
以下分析 patch 函数代码运行过程:
- 当运行到 patch 方法时
patch(n1, n2, container, anchor = null, parentComponent = null, parentSuspense = null, isSVG = false, optimized = false)其中 n1 即为 null,n2 即为要更新的 vnode,container 为#demo容器元素。 - 初始化运行时 n1 为 null, n2 为要更新的 vnode
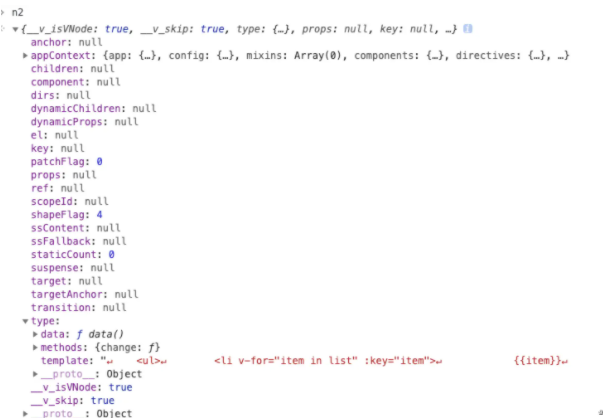
-
此时判断符合
shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT执行processComponent(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized)方法。 n1、n2 等参数同 patch 方法。 -
processComponent 方法
packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const processComponent = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
optimized: boolean
) => {
// 其他逻辑
// 首次渲染执行此方法
mountComponent(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
}
// 其他逻辑
}
由于是首次渲染我们调用 mountComponent 方法, 以下为 mountComponent 源码:
packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const mountComponent: MountComponentFn = (
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance = (initialVNode.component =
// 1. 调用createComponentInstance生成对当前n2的实例
createComponentInstance(initialVNode, parentComponent, parentSuspense))
// 2. 初始化 props 和 slots 调用组件的 setup 方法
setupComponent(instance)
// 3. instance为上面生成的实例,initialVNode还是为上图n2,container为#demo,其他为默认值
setupRenderEffect(
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
}
setupComponent 实现逻辑如下
packages/runtime-core/src/component.ts
export function setupComponent(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
isSSR = false
) {
isInSSRComponentSetup = isSSR
const { props, children, shapeFlag } = instance.vnode
const isStateful = shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
// 1. 初始化 props 和 slot 所以在 data 或者 setup 时是可以访问 props 的
initProps(instance, props, isStateful, isSSR)
initSlots(instance, children)
// 2. 执行 setupStatefulComponent 执行 setup 方法(前提是组件配置了 setup 的钩子函数)
const setupResult = isStateful
? setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR)
: undefined
isInSSRComponentSetup = false
return setupResult
}
setupRenderEffect 实现逻辑如下:
packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const setupRenderEffect: SetupRenderEffectFn = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
// create reactive effect for rendering
instance.update = effect(function componentEffect() {
// instance.isMounted;如果已经渲染,则走更新逻辑;则走未渲染的逻辑
if (!instance.isMounted) {
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | null | undefined
const { el, props } = initialVNode
const { bm, m, parent } = instance
// beforeMount hook
// 1. 先调用了当前实例的beforeMount钩子函数
if (bm) {
invokeArrayFns(bm)
}
// onVnodeBeforeMount
// 2.调用n2的父类的BeforeMount钩子函数
if ((vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeBeforeMount)) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parent, initialVNode)
}
// 其他逻辑
// 3. 调用renderComponentRoot函数进行渲染组件的根元素
const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))
// 其他逻辑
// 4. 调用patch subtree 为上面生成的根 node
patch(
null,
subTree,
container,
anchor,
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
initialVNode.el = subTree.el
// 5.调用当前实例的mounted钩子函数
if (m) {
queuePostRenderEffect(m, parentSuspense)
}
// onVnodeMounted
// 6.调用n2的父类的mounted钩子函数;
if ((vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeMounted)) {
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook!, parent, initialVNode)
}, parentSuspense)
}
const { a } = instance
if (
a &&
initialVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE
) {
// 7.调用当前实例的activated钩子函数;不是直接调用,而是通过queuePostRenderEffect放到队列中去调用
queuePostRenderEffect(a, parentSuspense)
}
// 8. 最终把实例的isMounted置为true
instance.isMounted = true
}
// 其他逻辑
}, __DEV__ ? createDevEffectOptions(instance) : prodEffectOptions)
}
上面 componentEffect 函数中调用 patch 才是正式渲染的开始,前面大部分都是相当于数据的整理:
- 此时 subTree type 为 ul,在 patch 方法内部执行 processElement 方法
const processElement = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
optimized: boolean
) => {
isSVG = isSVG || (n2.type as string) === 'svg'
// 其他逻辑
mountElement(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
// 其他逻辑
}
mountElement 源码如下:
const mountElement = (
vnode: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
optimized: boolean
) => {
let el: RendererElement
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | undefined | null
const {
type,
props,
shapeFlag,
transition,
scopeId,
patchFlag,
dirs
} = vnode
el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(
vnode.type as string,
isSVG,
props && props.is
)
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
// 如果子集是文本直接渲染
hostSetElementText(el, vnode.children as string)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
// 如果子集是数组 继续渲染
mountChildren(
vnode.children as VNodeArrayChildren,
el,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG && type !== 'foreignObject',
optimized || !!vnode.dynamicChildren
)
}
}
- mountChildren 方法其实是遍历上面的
vnode.children继续调用 patch 方法 - 此时 patch 新的 n2 的类型是
Symbol(Fragment)执行 processFragment 方法
const processFragment = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
optimized: boolean
) => {
// 其他逻辑
if (n1 == null) {
hostInsert(fragmentStartAnchor, container, anchor)
hostInsert(fragmentEndAnchor, container, anchor)
// 执行 mountChildren
mountChildren(
n2.children as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
fragmentEndAnchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
} else {
// 其他逻辑
}
}
- 此时再次执行 mountChildren,再次依次执行 patch 方法
- 此时 patch 方法 n2 为 type 为 li, 执行 processElement 依次类推
上面所有的步骤执行完成,现在数据已经呈现到页面上,此时基本所有的事情都干完了,也就是相当于主队列空闲了,调用 flushPostFlushCbs()开始执行队列里面的函数,最后把 container 的_vnode 属性指向当前 vnode;方便下次做 dom diff 使用, 第一次渲染运行完成。
mount 的大体流程图如下: